31st October, 2023
Article by Dr. Trevor Clohessy

Blockchain: More than Just a Database
Blockchain, frequently lauded as a revolutionary technology, embodies a form of distributed ledger that sustains an expanding series of records (or blocks) securely connected through cryptographic hashes. Each block encapsulates a cryptographic hash of the preceding block, a timestamp, and transaction information, constructing a chain that is intrinsically robust against data alteration post-recording.
This technology underpins the establishment of a collective, unalterable ledger that streamlines the documentation of transactions and monitoring of assets within a business ecosystem. Such assets could span tangible entities like real estate, vehicles, money, and land, or intangible assets such as intellectual property, patents, and copyrights.
Blockchain: Underneath the Hood
The core characteristics of blockchain lay the foundation for its manifold advantages to the business realm. For example, supply chains represent a natural set of use cases for blockchain technology.
Figure 1 below illustrates a blockchain-integrated business process for a typical transaction. The process begins with the “Customer” placing an order on the “Blockchain Platform”. Upon receiving the order, the platform initiates a “Smart Contract” to automate and secure the transaction. A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. It ensures that all parties involved in the contract adhere to the agreed-upon terms without the need for intermediaries.
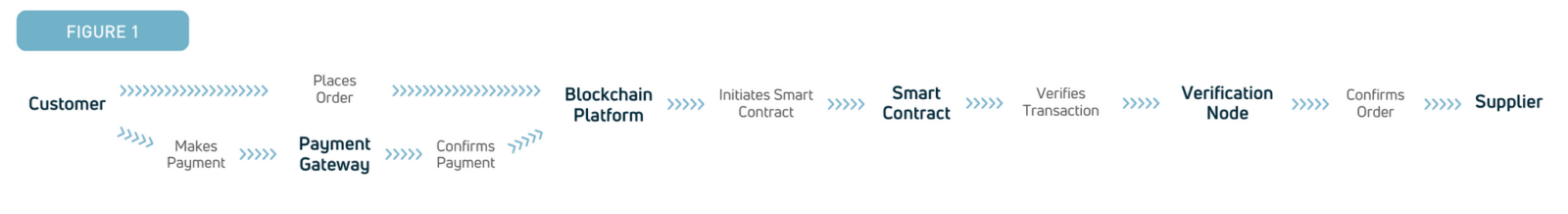
This contract is then verified by a “Verification Node” to ensure its authenticity and adherence to the agreed terms. Once verified, the order is confirmed and passed on to the “Supplier”. Simultaneously, the customer makes a payment through the “Payment Gateway”, which upon successful transaction, sends a confirmation back to the blockchain platform. This integrated approach ensures a transparent, secure, and efficient transaction process, leveraging the power of blockchain technology and the trustworthiness of smart contracts.
Blockchain Knowledge and Legitimization Gap
One challenge teaching blockchain technology that I often encounter is the legitimization of the technology and a lack of understanding of how blockchain can be applied in organisations. The different stages of blockchain evolution might perplex leaders, leading to a lack of understanding of its full potential or relevance to their organisation.
This misunderstanding can result in the misallocation of resources to outdated or irrelevant blockchain technologies. Moreover, the confusion can foster resistance among stakeholders, inhibiting the necessary organisational change for blockchain adoption. On the regulatory front, a lack of clarity about the evolution may cause compliance issues if the organisation adopts a blockchain technology that doesn’t adhere to legal and regulatory standards.
Additionally, confusion can hinder the development of necessary skills and expertise within the organisation to leverage blockchain technology effectively. One technique I use to teach students is to showcase the evolution of blockchain technology (table below) from 2008 to its current evolution: Blockchain 4.0 which is tailored towards mainstream business applications.
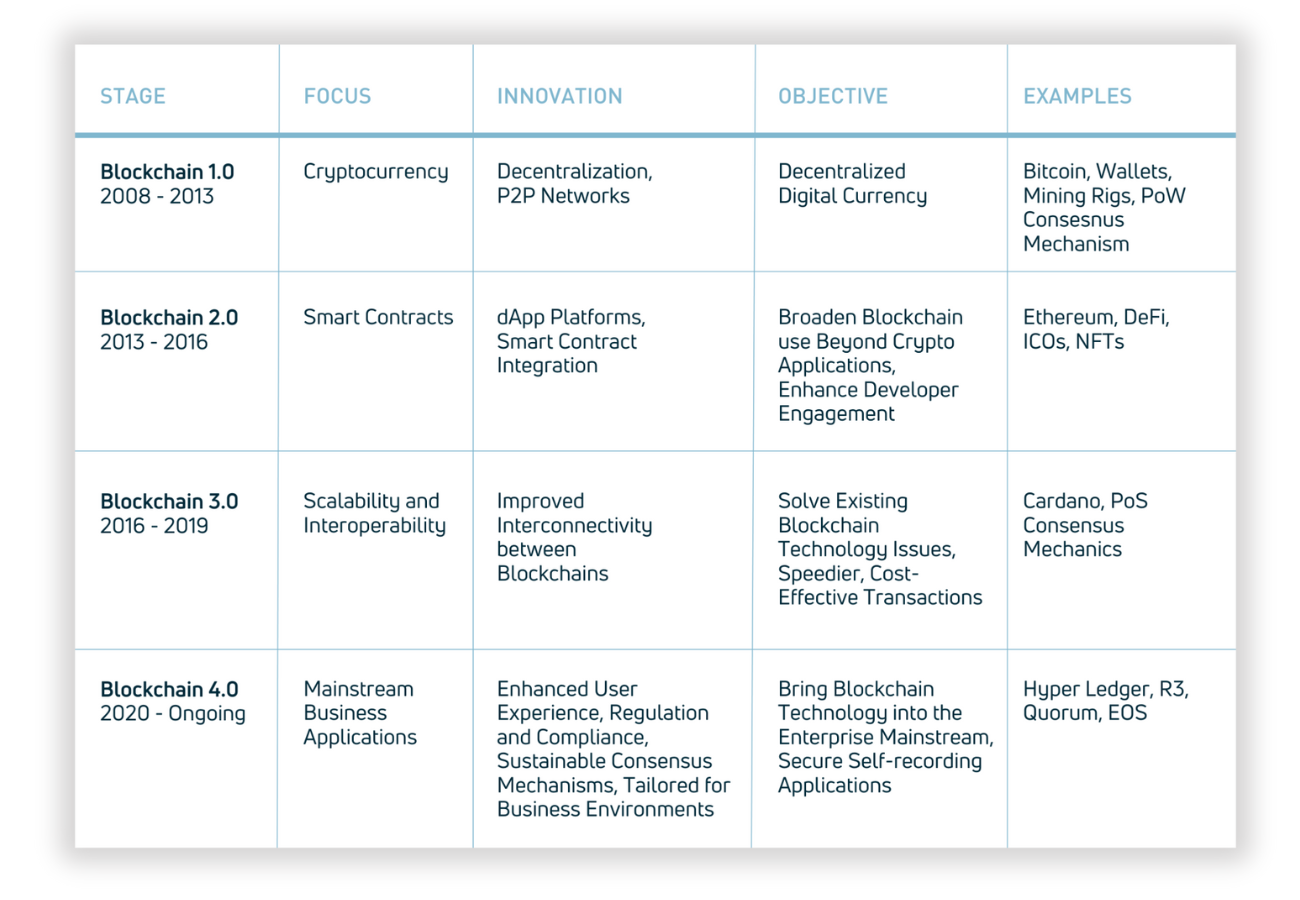
Blockchain 4.0: A New Era of Enterprise Innovation
As can be seen from the table above, each stage in the evolution of blockchain technology reflects a distinct focus and brings forth new features, goals, and examples or components illustrating the progression from a digital currency system to a mainstream business application platform. Each version of blockchain technology built upon the last, aiming to improve and expand upon existing capabilities.
Blockchain 1.0 laid the groundwork with the creation of Bitcoin, Blockchain 2.0 expanded the technology’s scope with the introduction of smart contracts via Ethereum, Blockchain 3.0 aimed at solving scalability and interoperability issues, and Blockchain 4.0 represents a significant step towards making blockchain technology more accessible and useful in mainstream business environments.
Leaders who understand this evolution are better positioned to lead their organisations through the digital transformation that blockchain technology can facilitate via the following:
- Competitive Advantage: Blockchain 4.0, with its focus on mainstream business applications, provides tools for creating secure, self-recording, and decentralised applications. Leaders who grasp these advancements can leverage them to gain a competitive edge, be it through streamlined processes, reduced costs, or enhanced security and transparency.
- Long-term Vision: Understanding Blockchain 4.0 helps in developing a long-term vision regarding how blockchain can be integrated and leveraged for organisational growth and sustainability.
- Talent Attraction and Development: As blockchain technology continues to evolve, there will be a growing need for talent with expertise in blockchain applications. Leaders with a clear understanding of blockchain’s progression can better identify, attract, and develop the necessary talent to drive blockchain initiatives successfully.
- Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management: The regulatory environment around Blockchain 4.0 is evolving. Leaders need to understand blockchain’s trajectory to navigate regulatory compliance and manage associated risks effectively.
- Innovation and Adaptability: Understanding the Blockchain 4.0 fosters a culture of innovation and adaptability. Leaders can drive initiatives that explore blockchain applications relevant to their sector, encouraging a forward-thinking, innovative organisational culture.
Bridging the Blockchain Knowledge and Legitimization Gap
The Fundamentals of Blockchain Technology course offered by Technology Ireland ICT Skillnet and ATU Galway City aims to provide a thorough understanding of blockchain technology and Blockchain 4.0 and its applications across various industries.
- Gain a strong foundational understanding of blockchain technology and Blockchain 4.0
- Explore Blockchain’s 4.0 potential applications within their respective industries
- Understand the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding Blockchain 4.0
- Learn how blockchain 4.0 can integrate with other emerging technologies
- Be better prepared to drive Blockchain 4.0 initiatives within their organisations
Ultimately the course will enable leaders to foresee how Blockchain 4.0 could shape the future of their industries and foster strategic innovation within their organisations.
About the Author

Dr. Trevor Clohessy is a highly accomplished academic, with extensive experience in teaching, research, and professional service in blockchain. He holds a Ph.D. in Digital Transformation from the University of Galway, as well as an M.A. in Teaching and Learning and a Higher Education Diploma in Lego Serious Play from INHRFACE in Denmark. Dr Clohessy’s teaching experience in blockchain is extensive, having taught at Atlantic Technological University Galway, Charted Accountants Ireland, City Colleges Dublin, and the University of Galway. He is the Chair of the Blockchain Ireland Education, Skills, and Innovation Working Group and a Scientific Committee Member of the British Blockchain Association. He founded the Blockchain Expert Insights Podcast and the Novoverse Undergraduate Research Journal.
Unlock New Opportunities with Blockchain
Blockchain skills are continually in high demand and blockchain specialists are needed now more than ever to bridge critical skills gaps.
Learn More About Blockchain Courses with ICT Skillnet

